
Acquiring a high-quality signal during registration is critical to the results of every study. In the case of fNIRS measurement, a robust cardiac signal visible at both wavelengths is considered a clear indicator of good optode-scalp coupling.
However, observing signal characteristics during recording can be challenging. Especially when conducting measurements on multiple channels is needed. Therefore, in the new version of CortiView, we have added real-time signal quality measurement. It is based on the scalp coupling index (SCI). SCI is based on the cross-correlation across signal measurement wavelengths in the frequency range of cardiac signals(1). The result can be interpreted that the higher the correlation coefficient, the better the optode-scalp coupling is on this channel. In the new CortiView, you can find signal quality measurements in two locations:
- As a button, “Signal Quality” in the main application window. There each channel is marked in red “low”, yellow “medium”, or green “high” depending on the degree of signal correlation. You can quickly identify a channel with a poor optode-scalp coupling on your montage. If you do so – check if the optodes stick correctly to the scalp. This is a convenient option when preparing the subject for registration.
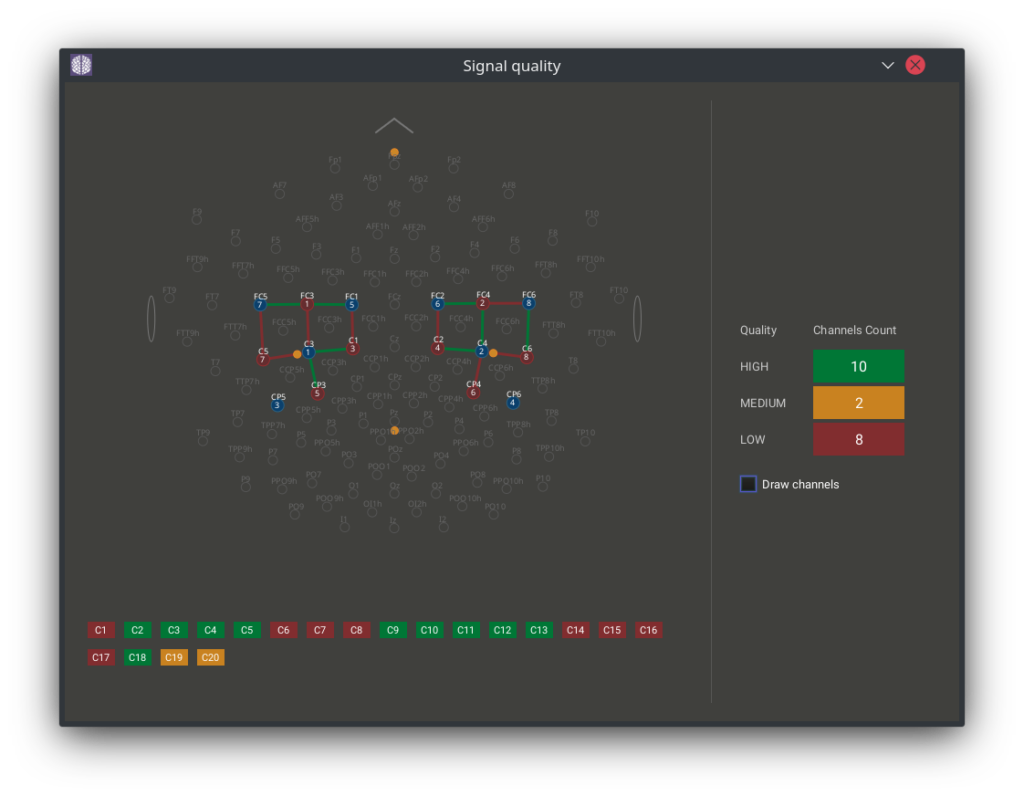
2. As a “tick” marked with red, yellow, or green next to the selected channel. The signal quality is checked every 5 seconds so that you can monitor the quality of individual channels in real time during recording.
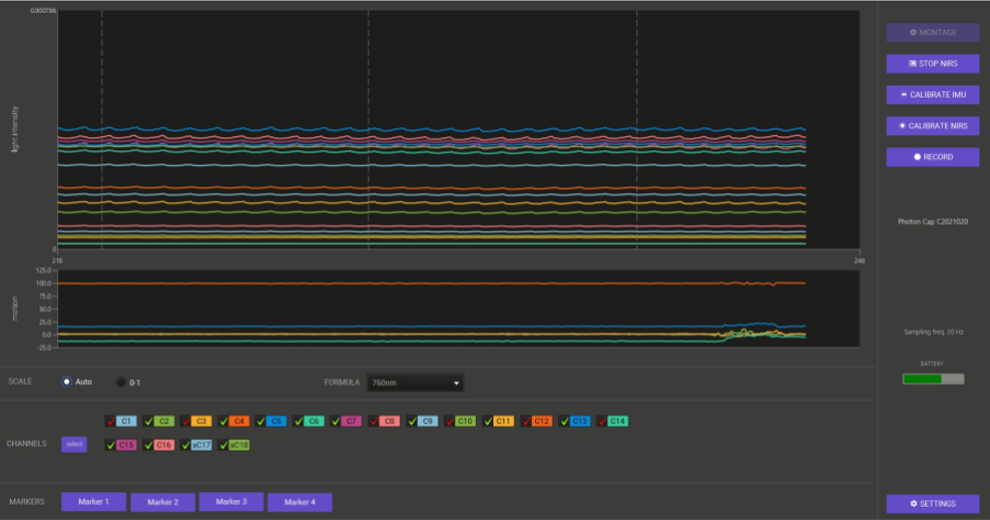
Thresholds for labelling channels as high/medium/low you can always customise in the “Settings” window. If you have questions about this feature, please contact our support.
Reference:
(1) Pollonini, L., Olds, C., Abaya, H., Bortfeld, H., Beauchamp, M. S., & Oghalai, J. S. (2014). Auditory cortex activation to natural speech and simulated cochlear implant speech measured with functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Hearing research, 309, 84-93.