Multimodality
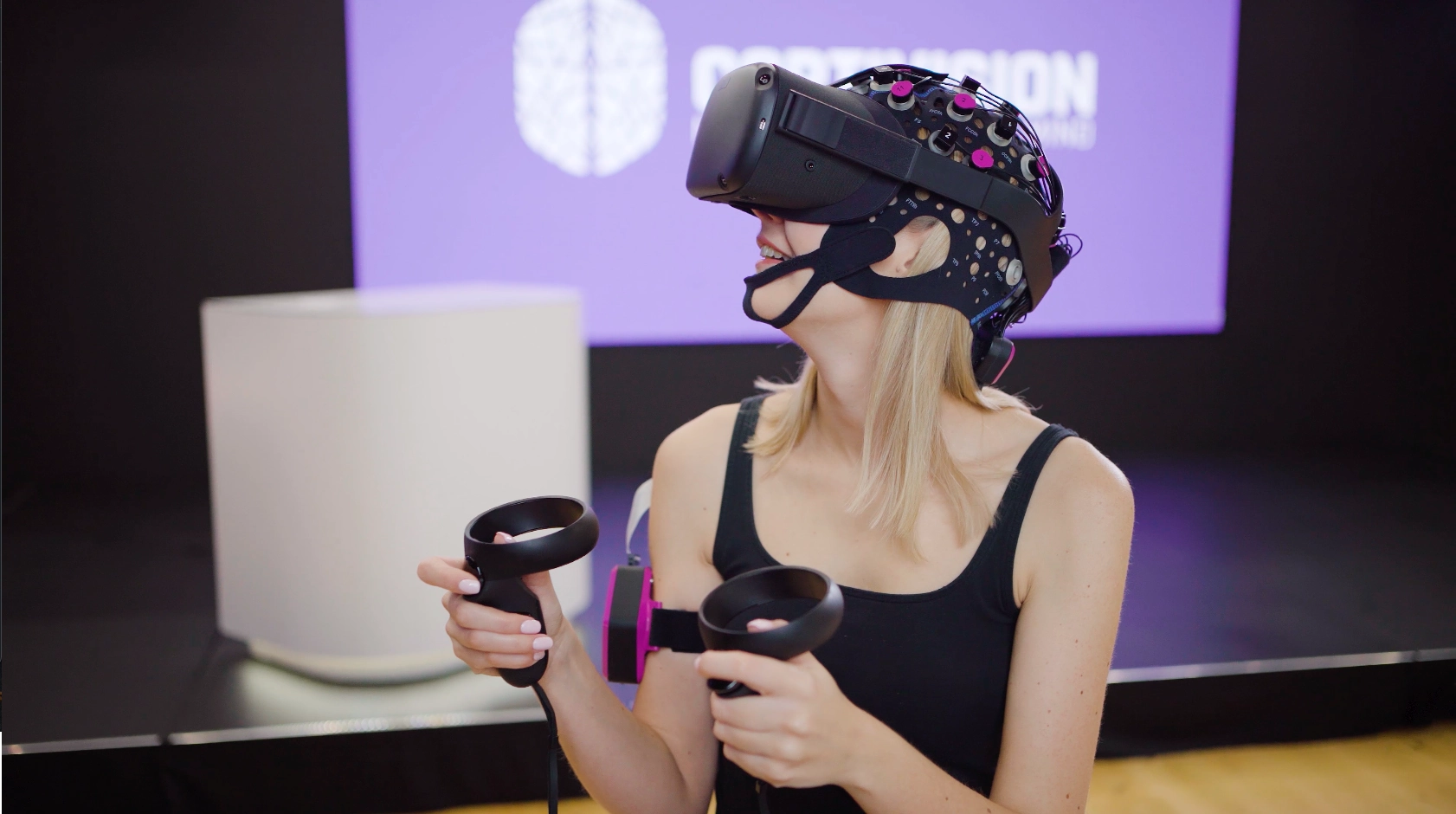
allowing for simultaneous measurement of neural dynamics (EEG) and cerebral blood flow (fNIRS), providing a complete picture of brain processes—ideal for studying cognitive workload, emotional states, or neurological disorders.
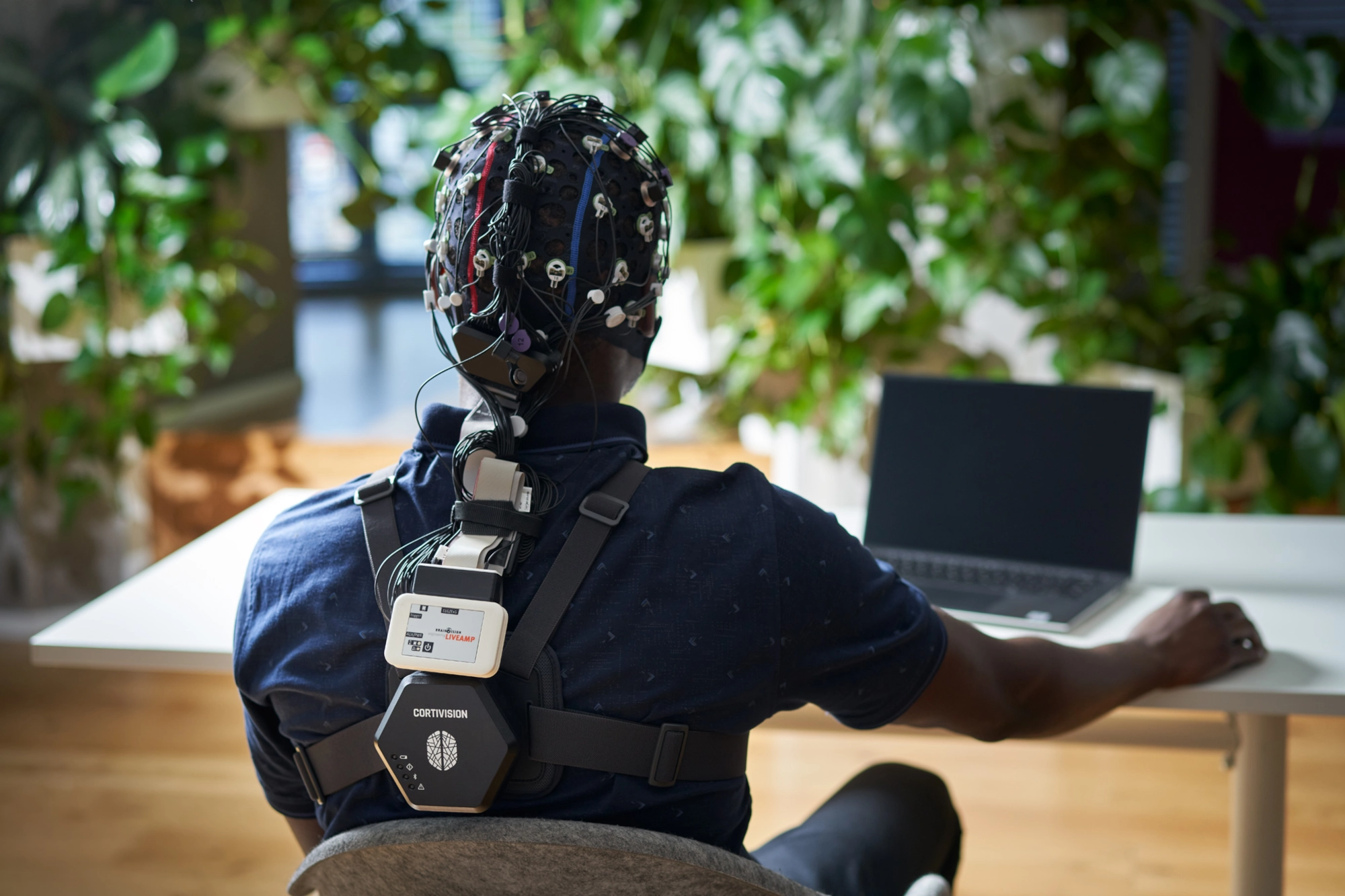
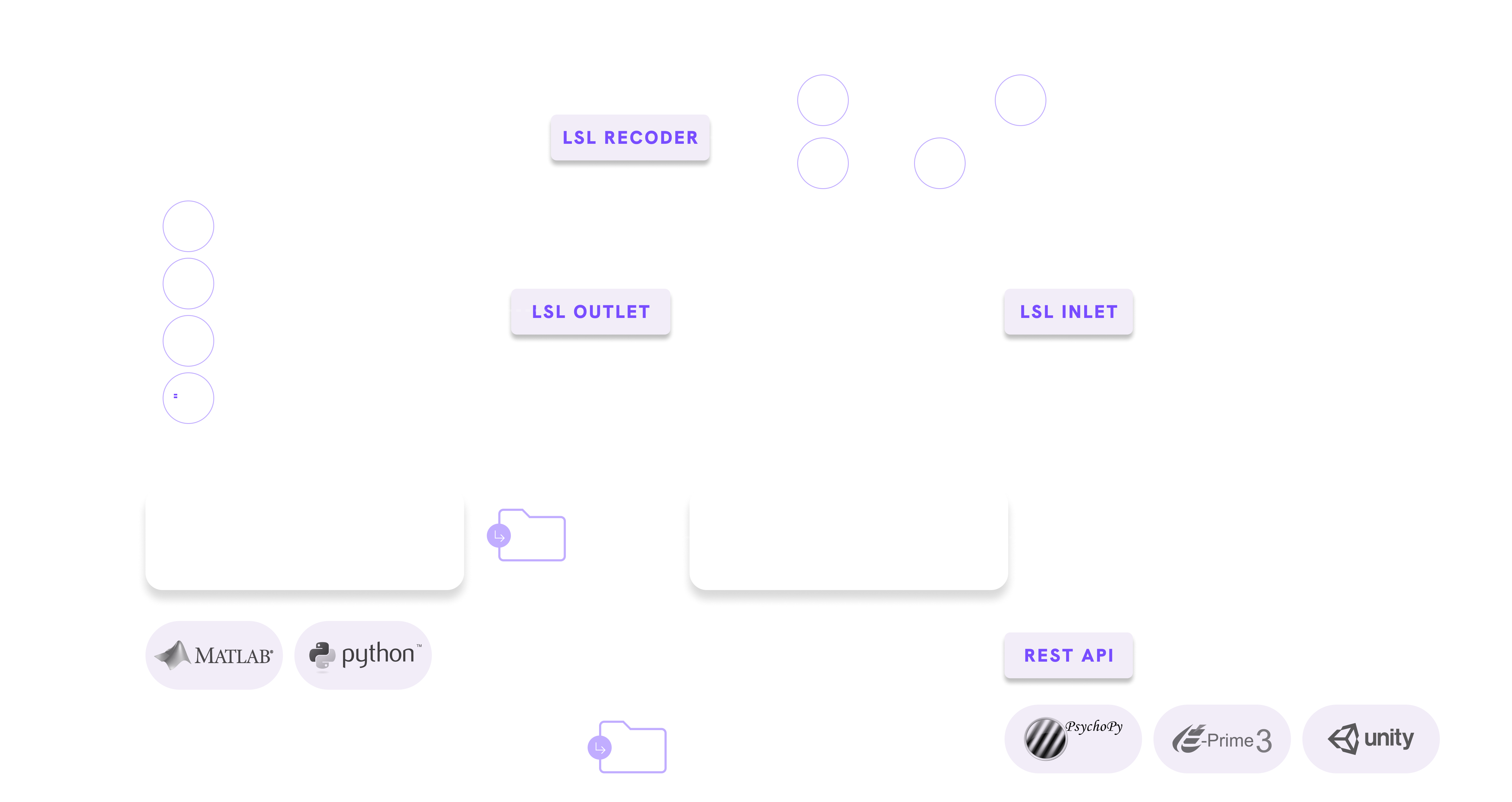
Cortivision and Brain Products have joined forces to combine functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) and electroencephalography (EEG). This fusion combines EEG's high temporal resolution with fNIRS's spatial precision, offering a comprehensive view of brain activity. Our solution with a LiveAmp amplifier and Cortivision fNIRS systems allows for synchronised, portable brain monitoring, making it easier to do research in various of settings.

allowing for simultaneous measurement of neural dynamics (EEG) and cerebral blood flow (fNIRS), providing a complete picture of brain processes—ideal for studying cognitive workload, emotional states, or neurological disorders.
provided by remarkable spatial resolution of the signal while the LiveAmp excels in temporal resolution, capturing electrical changes at the millisecond level. Together, these systems provide robust, multimodal data sets that enable a richer understanding of neural activity and improve the reliability of findings.
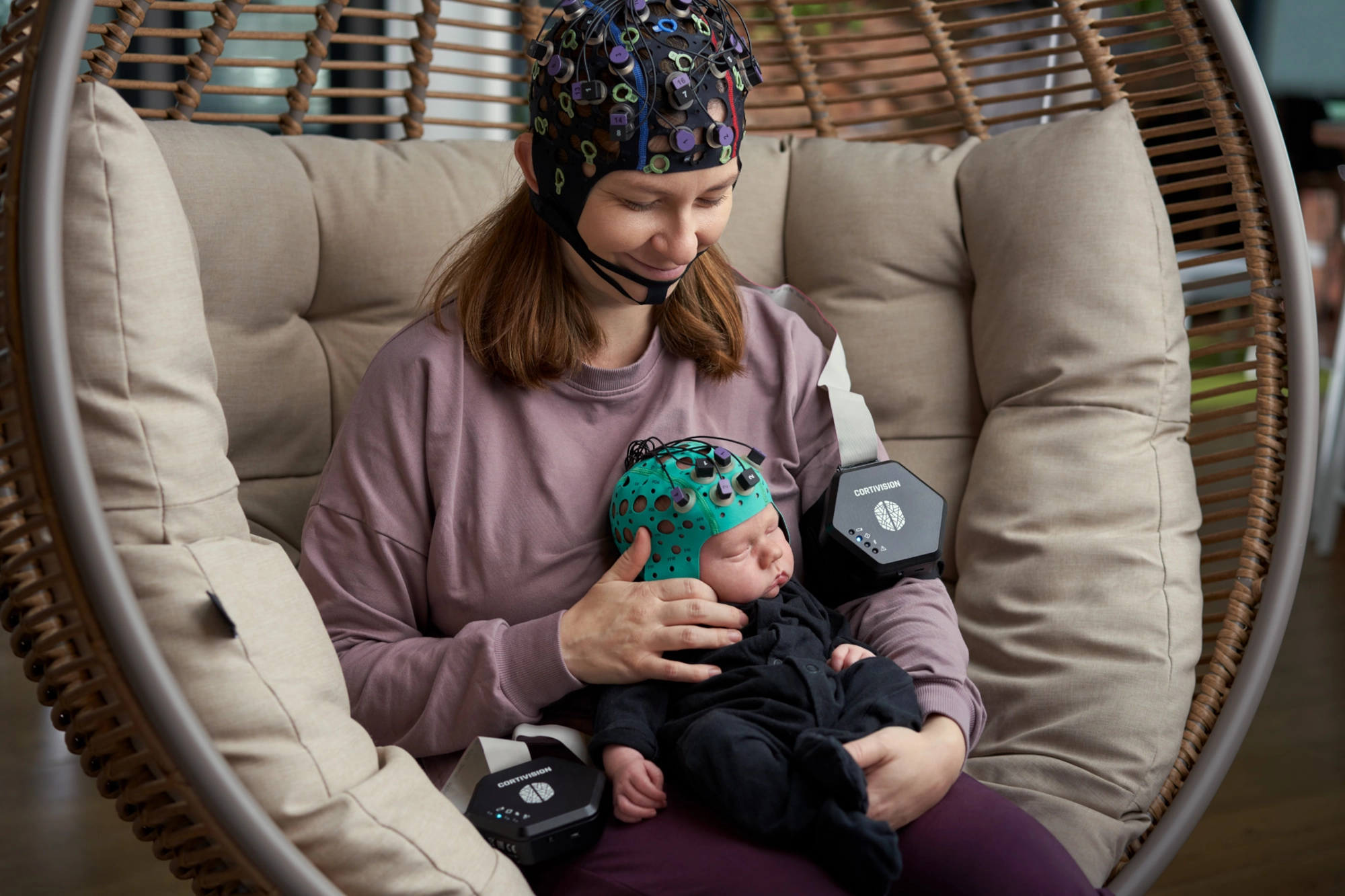
based on a wearable harness for mobile applications, perfect for real-world experiments with fNIRS. The LiveAmp system is lightweight and wireless, enabling high-quality EEG recordings in any environment.
thanks to compliance with both LiveAmp wireless and ActiChamp Plus high-performance stationary systems.Highest performance and precision of co-registration with the expansion to high-density EEG (up to 64 channels).
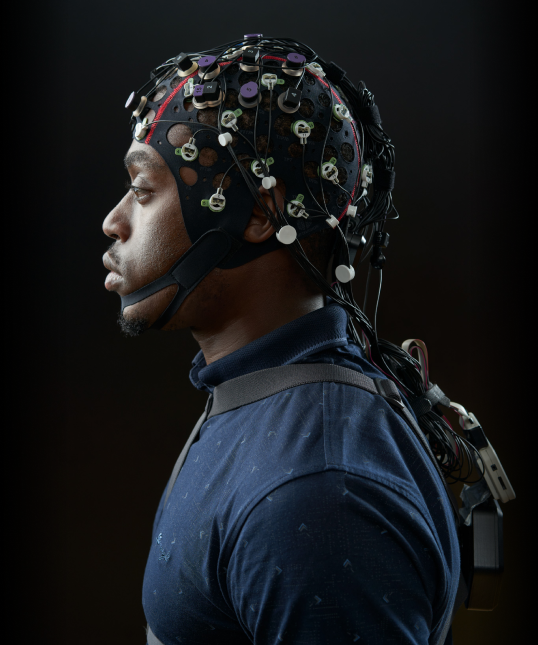

This multimodal approach delivers a more precise and comprehensive understanding of brain activity than relying on either method in isolation